Introduction
In the ever-changing world of marketing, businesses must continuously adapt to consumer needs and preferences. One effective strategy for achieving this is through the use of the STP (Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning) model. The STP model involves a three-step process that helps businesses to identify and cater to specific groups of consumers, resulting in increased customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and profits. In this article, we will explore the STP model, its components, and how it can be applied in different industries.
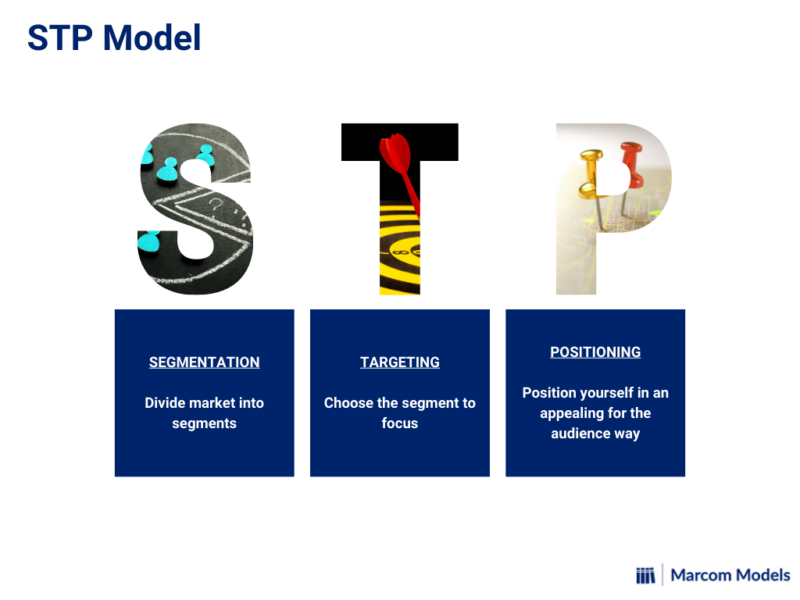
Segmentation
Segmentation is the first step in the STP model, and it involves dividing a larger market into smaller groups of consumers with similar characteristics and needs. By segmenting the market, businesses can better understand their customers and tailor their products or services to meet their specific demands. There are several different ways to segment a market, including demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral segmentation.
For example, a company that sells athletic shoes may segment their market based on demographics such as age, gender, and income. They may also use geographic segmentation to target consumers in specific regions or psychographic segmentation to focus on consumers who value health and fitness.
Targeting
After identifying segments in the market, the next step is targeting. This involves selecting specific segments that the business will focus on and developing marketing strategies that appeal to these groups. Targeting allows businesses to allocate resources more efficiently and effectively, resulting in better marketing ROI and customer satisfaction.
For instance, a car manufacturer may target a segment of customers who value eco-friendliness and fuel efficiency. They may develop marketing campaigns that emphasize the fuel efficiency of their cars and highlight their commitment to environmental sustainability.
Positioning
Positioning is the final step in the STP model, and it involves developing a unique brand image and value proposition that differentiates the business from its competitors. This is achieved by creating a distinctive and favorable perception of the business in the minds of consumers. The positioning strategy is crucial as it helps to establish a competitive advantage for the business.
For instance, Apple Inc. has positioned itself as a premium brand that offers high-quality products with innovative design features. This positioning has helped the company to differentiate itself from competitors and attract a loyal customer base that values quality and innovation.
Application of STP Model
The STP model can be applied in various industries, from retail and hospitality to healthcare and finance. In the hospitality industry, for example, hotels can use the STP model to segment their market based on the needs and preferences of different types of travelers, such as business travelers, families, and solo travelers. They can then develop targeted marketing campaigns and services that cater to these specific groups.
In the healthcare industry, the STP model can be used to segment patients based on their health needs, age, and income. Healthcare providers can then develop personalized healthcare plans that cater to the specific needs of each patient.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the STP model is a powerful tool for businesses to develop effective marketing strategies that cater to the needs and preferences of their customers. By segmenting the market, targeting specific groups, and positioning themselves favorably in the minds of consumers, businesses can establish a competitive advantage and increase customer satisfaction, loyalty, and profits. The application of the STP model in various industries has proven to be successful, and its implementation can greatly benefit any business looking to increase its market share and profitability.
References
Andaleeb, S. S. (2016). Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning. Strategic Marketing Management in Asia, 179–207. https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-78635-746-520161006
Bigo, C., Raj, A., & Situmeang, R. R. (2021). Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning (STP), Communication and Price Strategies on Consumer Purchasing Decisions at PT. Alfa Scorpii Medan. Jurnal Mantik, 4(4), 2370–2375. https://doi.org/10.35335/mantik.vol4.2021.1165.pp2370-2375
Islam, M. T. (2021). Segmenting, targeting and positioning in Islamic marketing. Journal of Islamic Marketing, 12(7), 1385–1404. https://doi.org/10.1108/jima-10-2018-0181
Moutinho, L. (2000). Strategic Management in Tourism. Oxford University Press, USA.
Schlegelmilch, B. B. (2022). Segmenting Targeting and Positioning in Global Markets. Management for Professionals, 129–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90665-8_6