Introduction
SWOT analysis is a widely used tool for strategic planning in both business and non-business settings. The acronym SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, and the analysis involves identifying and evaluating these four elements in relation to a particular situation or decision. While the SWOT analysis has been in use for several decades, there is still much to be learned about its use and effectiveness. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and applying the SWOT analysis model.
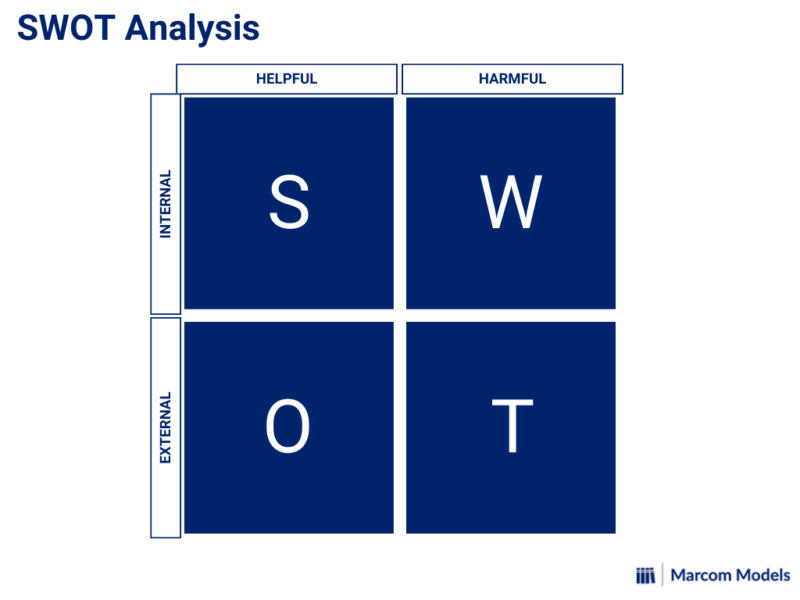
Understanding the SWOT Model
The SWOT model is used to evaluate the internal and external factors that affect an organization or individual. Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors that are under the control of the organization, while opportunities and threats are external factors that are beyond the organization’s control. The SWOT model is used to evaluate these factors and develop a strategic plan based on the results.
Strengths: Internal factors that are positive and under the control of the organization. These can include assets, expertise, reputation, and financial resources.
Weaknesses: Internal factors that are negative and under the control of the organization. These can include lack of resources, outdated technology, poor management, or inefficient processes.
Opportunities: External factors that are positive and beyond the control of the organization. These can include changes in the market, new technologies, or emerging trends.
Threats: External factors that are negative and beyond the control of the organization. These can include changes in regulations, competition, or economic conditions.
Applying the SWOT Model
The SWOT model is used to develop a strategic plan based on the results of the analysis. This plan should take into account the strengths and weaknesses of the organization, as well as the opportunities and threats in the external environment. The following are the steps involved in applying the SWOT model:
Step 1: Define the objective of the analysis. This could be a new project, a business decision, or a strategic plan.
Step 2: Identify the internal strengths and weaknesses of the organization. This could be done through a self-assessment, surveys, or interviews.
Step 3: Identify the external opportunities and threats that affect the organization. This could be done through market research, competitor analysis, or environmental scans.
Step 4: Evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to determine the organization’s strategic position.
Step 5: Develop a strategic plan based on the results of the analysis. This plan should take into account the organization’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as the opportunities and threats in the external environment.
Criticism of the SWOT Model While the SWOT analysis is a widely used tool, it is not without its limitations and criticisms. Some of the criticisms include:
Misuse: The SWOT model is often misused by organizations that do not understand its purpose or use it as a checklist rather than a strategic planning tool.
Limitations: The SWOT model is limited in that it does not provide a detailed analysis of the external environment or account for the interrelationships between different factors.
Comparison to other models: Some argue that other strategic planning models, such as PESTLE or Porter’s Five Forces, provide a more comprehensive analysis of the external environment.
Conclusion
SWOT analysis is a widely used tool for strategic planning in both business and non-business settings. While it has its limitations and criticisms, the SWOT model can be a valuable tool when used correctly. By understanding the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing an organization or individual, a strategic plan can be developed that takes into account the internal and external factors that affect the situation. As with any strategic planning tool, the SWOT model should be used in conjunction with other models and frameworks to provide a comprehensive
References
Sabbaghi, A., & Vaidyanathan, G. (2004). SWOT analysis and theory of constraint in information technology projects. Information systems education journal, 2(23), 1-19. http://scholar.googleusercontent.com/scholar?q=cache:L6Owx-10GegJ:scholar.google.com/+swot+analysis+theory&hl=nl&as_sdt=0,5
Almutairi, K. M., Dehshiri, S. J. H., Dehshiri, S. J. H., Mostafaeipour, A., Hoa, A. X., & Techato, K. (2021). Determination of optimal renewable energy growth strategies using SWOT analysis, hybrid MCDM methods, and game theory: A case study. International Journal of Energy Research, 46(5), 6766–6789. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7620
Helms, M. M., & Nixon, J. (2010). Exploring SWOT analysis – where are we now? Journal of Strategy and Management, 3(3), 215–251. https://doi.org/10.1108/17554251011064837
Leiber, T., Stensaker, B., & Harvey, L. (2018). Bridging theory and practice of impact evaluation of quality management in higher education institutions: a SWOT analysis. European Journal of Higher Education, 8(3), 351–365. https://doi.org/10.1080/21568235.2018.1474782
Madsen, D. Ø. (2016, March 21). SWOT Analysis: A Management Fashion Perspective. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2615722
Puyt, R. W., Lie, F. B., & Wilderom, C. P. (2023). The origins of SWOT analysis. Long Range Planning, 102304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2023.102304
Suh, J. (2014). Theory and reality of integrated rice–duck farming in Asian developing countries: A systematic review and SWOT analysis. Agricultural Systems, 125, 74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2013.11.003